Explore the advantages and disadvantages of traditional economy: from subsistence-level production to sustainable resource management. Learn the key differences between cultural customs and modern economies with this blog post.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Economy: A Comprehensive Guide
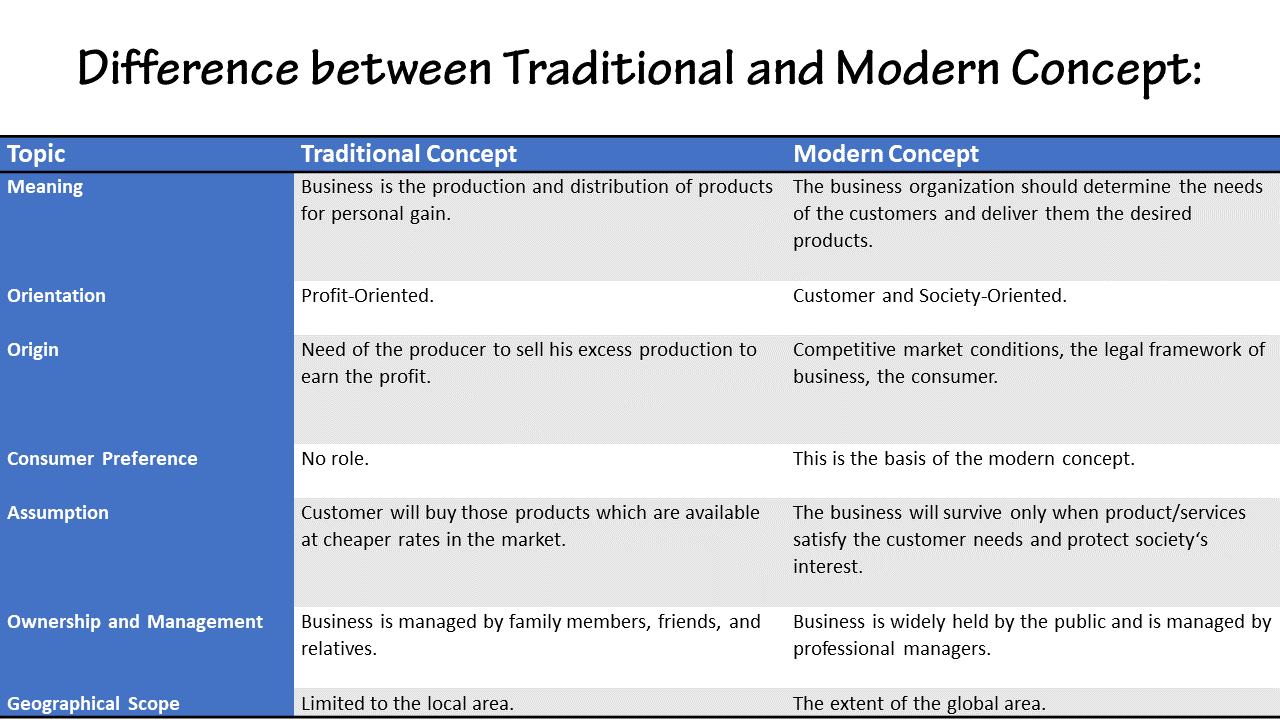
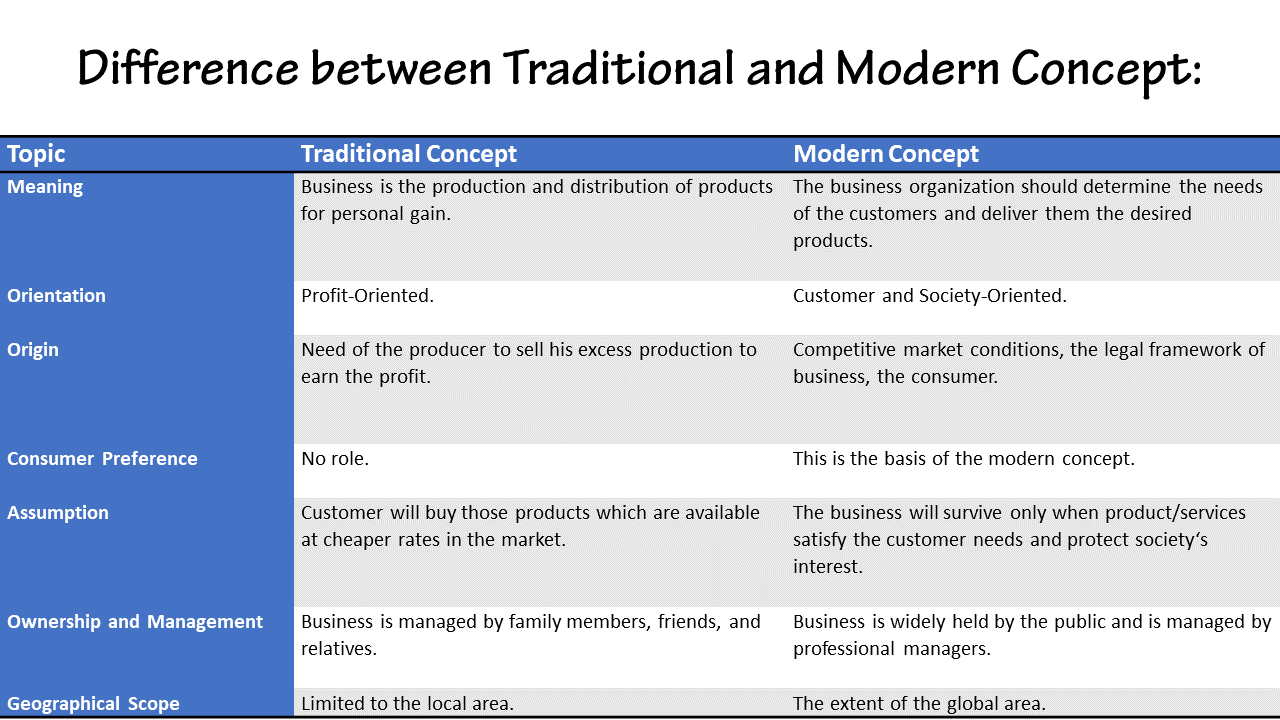
A traditional economy is an economic system that relies on customs, traditions, and cultural beliefs to determine the production, consumption, and distribution of goods and services. In a traditional economy, economic decisions guide by long-standing customs and practices that have stood passed down from generation to generation. This type of economy often found in rural and indigenous communities. Where the way of life deeply rooted in traditional practices and where self-sufficiency and sustainability are prioritized.
In a traditional economy, people often engage in subsistence agriculture and hunting, rely on barter for trade, and have limited access to modern technology. While traditional economies may face challenges in the face of globalization and modernization. Also, They have advantages in promoting social cohesion, preserving cultural heritage, and sustainable resource management.

Introduction to Traditional Economy
A traditional economy is an economic system that relies on customs, traditions, and cultural beliefs to determine the production, consumption, and distribution of goods and services. This type of economy primarily found in rural and indigenous communities. Where the way of life deeply rooted in traditional practices and customs. Also, Traditional economies have existed for centuries, enabling communities to sustain themselves and preserve their cultural heritage. Study of Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Economy below are;
Characteristics of Traditional Economy
- Barter System: In a traditional economy, the barter system is often used for trade. Goods and services are exchanged directly, without the use of currency. Also, This mutual exchange allows for the satisfaction of diverse needs within the community.
- Subsistence Agriculture and Hunting: Agriculture and hunting are the primary means of sustenance in traditional economies. People grow crops and raise livestock for their consumption rather than for commercial purposes. Also, This self-sufficiency helps communities meet their basic needs without excessive reliance on external markets.
- Close-knit Community: Traditional economies are typically characterized by close-knit communities where cooperation and communal sharing are highly valued. Each member of the community contributes to the well-being of the whole, fostering a sense of social cohesion and collective responsibility.
- Limited Technological Advancements: Traditional economies often have limited access to modern technology and rely on traditional tools and techniques for production. While this may limit productivity compared to technologically advanced economies, it also ensures the preservation of traditional skills and practices.
- Custom and Tradition: Economic decisions in traditional economies stand guided by customs, traditions, and societal norms, which pass down from generation to generation. These customs help maintain social order and provide a sense of continuity and identity within the community.
- Limited Division of Labor: There is a limited division of labor in traditional economies. With most individuals performing a wide range of tasks necessary for survival. This fosters a sense of self-sufficiency and interdependence among community members.
- Sustainability and Resource Management: Traditional economies emphasize sustainable practices and resource management to ensure the long-term well-being of the community. They often have intricate knowledge of local ecosystems and implement strategies for preserving natural resources and maintaining environmental balance.
Advantages of Traditional Economy
- Social Cohesion and Community Identity: Traditional economies emphasize strong social ties and community cooperation. The reliance on communal resources and interdependence fosters a sense of unity and collective responsibility. Traditional economic activities often involve shared labor, mutual support, and reciprocal relationships. Leading to a tightly-knit community where cultural traditions and values are preserved.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Traditional economies have historically developed sustainable practices for managing natural resources. They often have a deep understanding of local ecosystems and employ techniques that prioritize long-term resource preservation. Also, This focus on sustainability helps prevent overexploitation and ensures the continued availability of resources for future generations.
- Reduced Dependence on Cash Economy: Traditional economies often rely less on cash-based transactions and instead favor bartering or non-monetary exchanges. This can be advantageous in regions where cash is scarce or inaccessible. Bartering allows communities to meet their needs by exchanging goods and services directly. Enabling resource distribution without the need for extensive monetary transactions.
- Preserving Cultural Heritage: Traditional economies are intimately tied to cultural values, rituals, and practices. These economies often provide a platform for the preservation and transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. By engaging in traditional economic activities, communities can maintain their unique identity, protect traditional knowledge systems, and pass on essential skills and crafts.
Disadvantages of Traditional Economy
- Limited Economic Growth: Traditional economies often experience limited economic growth and development. This is due to their focus on subsistence and the absence of market-oriented activities. Without a formal market structure, it becomes difficult to accumulate capital and invest in productivity-enhancing technologies. As a result, traditional economies may struggle to generate substantial wealth and expand their economic opportunities.
- Technological Disadvantage: Traditional economies face challenges in keeping up with technological advancements. The lack of access to modern tools, machinery, and knowledge can hinder productivity and competitiveness. Without the means to adopt new technologies, traditional economies may find it difficult to increase production or engage in value-added activities. This technological gap can further isolate these economies from the benefits of globalization.
- Dependency on Natural Resources: Traditional economies heavily rely on natural resources for sustenance. This can be sustainable when resources are managed properly. It also makes these economies vulnerable to environmental changes and the depletion of resources. Factors such as climate change, deforestation, and overfishing present significant challenges to traditional livelihoods and the overall well-being of the community. This dependency can hinder long-term economic stability.
- Limited Access to Infrastructure and Services: Traditional economies often have limited access to modern infrastructure, healthcare, education, and other essential services. The lack of access to these services can perpetuate inequalities between traditional and urban communities. It can also hamper the socioeconomic development of traditional economies. Making it difficult for them to compete with more developed regions. This limited access to infrastructure and services can hinder the overall progress and well-being of the community.
Challenges of Traditional Economy
- Limited Economic Growth: Due to the focus on subsistence and lack of market-oriented activities. Traditional economies may experience limited economic growth and development. The absence of a formal market structure can hinder the accumulation of capital and investment in productivity-enhancing technologies.
- Technological Disadvantage: Traditional economies often struggle to keep up with technological advancements, which can hinder productivity and competitiveness. The lack of access to modern tools, machinery, and knowledge may limit their ability to increase production or engage in value-added activities.
- Dependency on Natural Resources: Traditional economies heavily rely on natural resources for sustenance. Making them vulnerable to environmental changes and depletion of resources. Factors such as climate change, deforestation, and overfishing can have detrimental effects on traditional livelihoods and the overall well-being of the community.
- Limited Access to Infrastructure and Services: Traditional economies may have limited access to modern infrastructure, healthcare, education, and other essential services. This lack of access can hinder socioeconomic development and perpetuate inequalities between traditional and urban communities.
Conclusion
Traditional economies play a significant role in preserving cultural heritage and sustainable practices. While they face challenges in a rapidly changing world, their emphasis on communal values, resource management, and adaptability continues to contribute to the resilience of many indigenous communities. Preserving and valuing traditional economies is crucial for maintaining cultural diversity, and environmental sustainability, and fostering inclusive development. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Economy? As we navigate toward a more interconnected global society, recognizing and respecting the contributions of traditional economies can help us strike a balance between progress and the preservation of ancient wisdom.