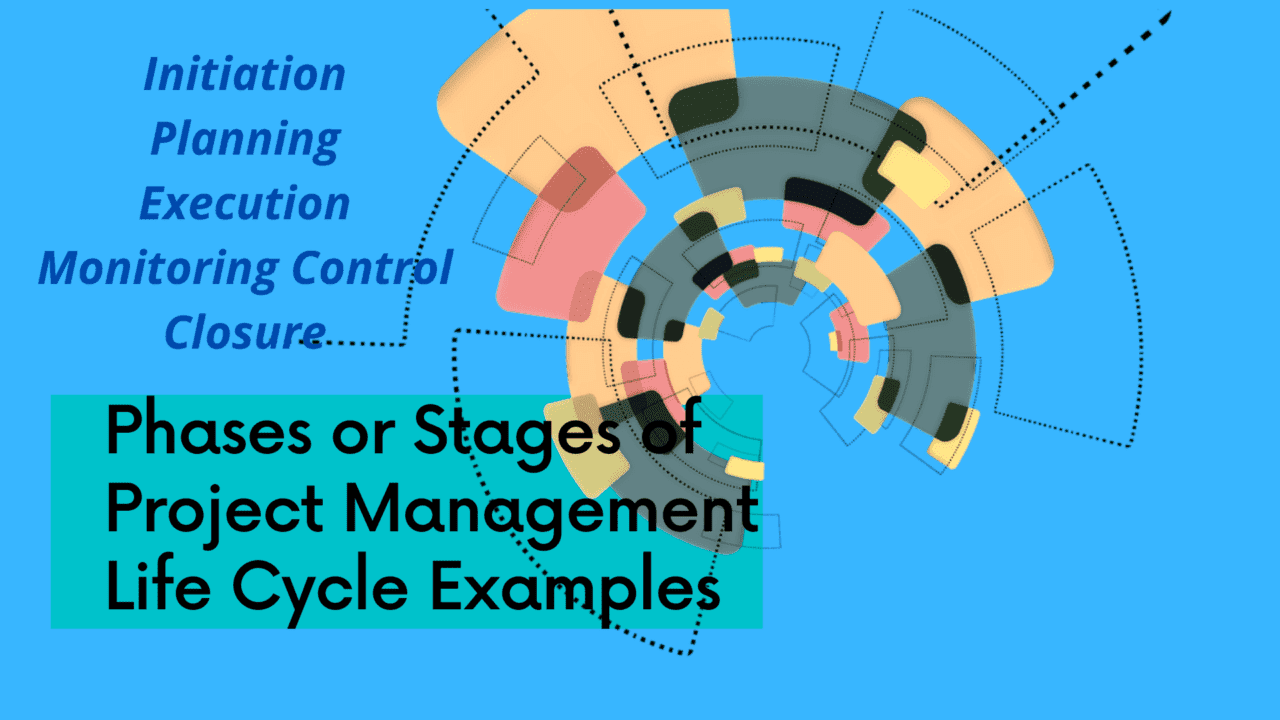
Project Management Life Cycle Stages and Phases with Examples Essay; Projects are part and parcel of our professional life. In the world of ever-changing technology and business trends, project management is in great demand. In this Topic, we are going to learn about the Project management life cycle. According to PMI, a project defines as temporary with a definite beginning and end in time. Also, the project is unique without routine operation and meant to meet the singular goal with a specific set of operations. PMI further defines project management as the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements.
What is the role of the project manager at each phase or stage of the Project Management Life Cycle? Why? What skills do you think are most important at each and why? What is the most important phase or stage?
Whether the project is software development, or new product launch, or even a movie; its management will progress through five life cycle phases. Understanding the project management lifecycle is valuable for successfully guiding a project from its initial stages to completion. No matter the project, the project management lifecycle can assist in narrowing the project’s focus; keeping its objectives in order, and finishing the project on time, on budget, and with a minimum of headaches.
The following are the roles of a PM in each of the phases or stages of the Project Management Life Cycle:
Project Initiation Phases or Stages;
In this initial phase, the PM begins multiple rounds of discussion with the stakeholders to decide whether the project can start. If all goes according to the plan Project initiation document create which outlines the requirements of the document. The PM gives the project’s overview in addition to the method that they want to utilize to achieve the results that desire. They also select the team members who require, depending on his or her skills and experience. The PM carries out assessments regarding risks, procurement, and also manages communication between stakeholders. At this phase, the manager needs to have risk assessment skills and cost estimation skills to guarantee that this phase is successful. The initiation phase of a project management cycle and a project life cycle involves:
- Conducting a feasibility study to assess the practicality of the project.
- Ascertaining the primary business need that the project will address.
- Aligning project objectives with those of the organization.
- Identifying stakeholders and their requirements, and.
- Develop a project brief or charter with all relevant details.
Many consider the initiation phase of the project life cycle the most significant of all the steps of project management. In the absence of proper initiation measures, projects are liable to fail or go off track. For a project to proceed to the next stage, stakeholders must approve the project charter.
Project Planning Phases or Stages;
In this stage, the PM is responsible for planning, and guaranteeing that there is a breakdown of the tasks from the beginning to the end of the project. The PM creates the roadmap of the whole project. Different goals and plans set by him/her such as scope, WBS, milestones, etc. The PM should make sure that appropriate budgets arrange for the project, and also that a risk assessment carries out. At this stage, the manager needs both budgeting and risk assessment skills. These abilities will make certain that the PM plans well according to the available resources; and, also predict the risks that the project might be dealing with down the road.
The goals of the project normally place following the SMART and/or the CLEAR methods. Goals-based on the SMART method is Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Timely; while goals based on the CLEAR method are Collaborative, Limited, Emotional, Appreciable, and Refinable. The planning phase of a project management cycle and project life cycle also involves:
- Identifying project milestones.
- Determining budget, time, and resource availability.
- Allocating tasks based on available resources.
- Establishing key performance indicators, and.
- Setting up a change management strategy.
Along with these, in the planning phase of a project life cycle, project managers must also develop a risk mitigation plan. Such a plan traces the potential risks and obstacles in the path of a project and includes strategies to overcome or minimize them.
Project Execution Phases or Stages;
At this stage, PM develops the team, assign resources, and daily meetings are taking place to track the progress. The PM should make sure that the project team has the resources that require to perform the project activities. The PM therefore observes and analyzes the work that is being done by the team. For the execution stage, the PM needs to have risk assessment skills. The manager should also embrace teamwork to make sure that the process of achieving the project runs smoothly.
The execution phase of both a project life cycle and a project management cycle is also recognized as the implementation phase. In this phase, the plan developed in the previous stage placing into action. Once the workflow has been established, project managers direct the execution of the project. They ensure the project is moving on track by holding status check meetings, adapting timelines according to project requirements; and communicating with everyone involved in the project, including stakeholders. A well-developed plan is crucial to the success of the execution phase.
The execution phase is the busiest among all the project life cycle phases; because this is where all the actual work performs. Managing the workforce is also an integral part of the execution phase. Project managers must not only ensure roles and responsibilities are being fulfilled; but, also keep their teams invested in the work they do through recognition, appreciation, and words of encouragement. In case of setbacks, managers must also prepare to fine-tune the project plan as needed and/or implement corrective actions. The execution phase is often the longest among all the phases of the project management life cycle.
Project Monitoring Control Phases or Stages;
Here the PM will utilize the Key Performance indicators to find out if the project is on track or not. The PM will recognize the issues in the project as it does performing. They should also ensure that the project meets the desired quality to satisfy all the stakeholders. The PM needs quality control and reporting skills to ensure that the project possesses the right quality. Reporting skills should help him to answer the various questions of the stakeholders.
Next in the steps of project management comes the monitoring and control phase. Among all project life cycle phases, this phase runs simultaneously with the execution phase. The monitoring and control phase of a project management cycle deals with performance measurement. The set key performance indicators are used to ascertain whether the project is progressing according to expectations and within budget. This is the stage where project managers control project costs, mitigate risks, evaluate roadblocks, strategize ways to overcome them, and monitor change requests.
Change requests happen when a team member, client, or stakeholder requests changes in terms of project deliverables that had been determined in the planning phase. It’s a project manager’s responsibility to ensure the change request aligns with the scope of the project; identify the resources required to implement the change; and, also decide whether approving the change request will be beneficial for the project in the long run.
Project Closure Phases or Stages;
Project closure is the final stage in both a project management cycle and a project life cycle. Of all the phases of the project management life cycle, this is where the project achieves completion. In this phase, project managers finalize and hand over project deliverables to the client, prepare a thorough project report, release resources, close contracts, and review project documentation to ensure everyone involved has received their dues.
Formally closing a project also requires project managers to announce the completion of the project to all relevant stakeholders, top-level management, and team members. At the end of it all, a reflection meeting, also known as a ‘post-mortem’, believes to recognize the success of the project and identify areas needing improvement. The performance of the project evaluates in terms of expenses incurred, adherence to timelines, and final project quality.
The diverse phases of the project management life cycle—from initiation to closure; provide managers with a structured approach to successfully track and deliver projects on time and within budget. Project life cycle phases are essential to controlling costs, promoting communication, and enhancing transparency within an organization.
At this stage, the role of the PM is to look into the things that are often overlooked, to ensure that the project carries to a proper conclusion. The PM will also organize workshop events to thank for the efforts done by the team members. The PM is also to do the post-mortem to analyze what went wrong in the project and should also write a review of the project to higher management. In this stage, the PM needs reporting and assessment skills to ensure that he evaluates the project for minor defects and also delivers a good report to the higher management.
An Examples;
Effective completion of all the stages of the project management life cycle requires project managers to be critical thinkers, efficient problem-solvers, and effective decision-makers. This is where Harappa’s Executing Solutions course comes in. This online strategy execution course will train you to handle the ins and outs of project management life cycle and project life cycle phases; while offering you some neat ideas on how to execute projects faster and better. You’ll be able to effortlessly take a solution from a mere idea to successful implementation; while learning to manage expectations, navigate roadblocks and calmly respond to crises.
Frameworks such as the Bifocal Approach will help you monitor projects by balancing short-term focus with long-term objectives. You’ll also learn the best ways to plan out your projects and create a roadmap for success, develop a mindset to tackle any obstacle you face, and efficiently delegate tasks to team members. Want to set an example before your team members and peers? Sign up today for Harappa’s Executing Solutions course!
Planning-Execution Merger;
The possibilities of issues and changes in requirements from the client in the execution phase can lead to change in the project plan. The planning is again carried out in the execution phase. The agile methodology that is widely used for software projects provides the flexibility to incorporate such last-minute changes. Large projects divide into small modules like manufacturing, and quality can be different modules for a product. Completion of one module can correspond with initiation for other projects. It can conclude that these stages are dynamic, but with the help of different tools for project management; we can ensure the successful completion of the project.
In our opinion, planning is the most important phase of the project management lifecycle; because it provides the PMs the opportunity to carry out an analysis of the underlying risks of the project. At the planning stage, all requirements gathering, the analysis makes, and the PM gets a better picture of the objective; which helps in project timelines and deliverables. This stage allows the PM to create a contingency plan. Planning saves time and also money that could use in all the other phases of the project.
Post Reference and Retrieved from; https://www.ukessays.com/essays/project-management/skills-and-role-of-a-project-manager.php?vref=1, https://harappa.education/harappa-diaries/project-management-life-cycle/, and https://www.educba.com/project-management-life-cycle/