Discover the differences between manual and computerized accounting systems. Learn how technology has revolutionized financial management practices. Explore the evolution of accounting systems from manual to computerized methods. Understand the key differences, benefits, and limitations of manual and computerized accounting systems. Discover how technology has revolutionized financial management, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and scalability in businesses of all sizes.
Meaning of Manual and Computerized Accounting Systems
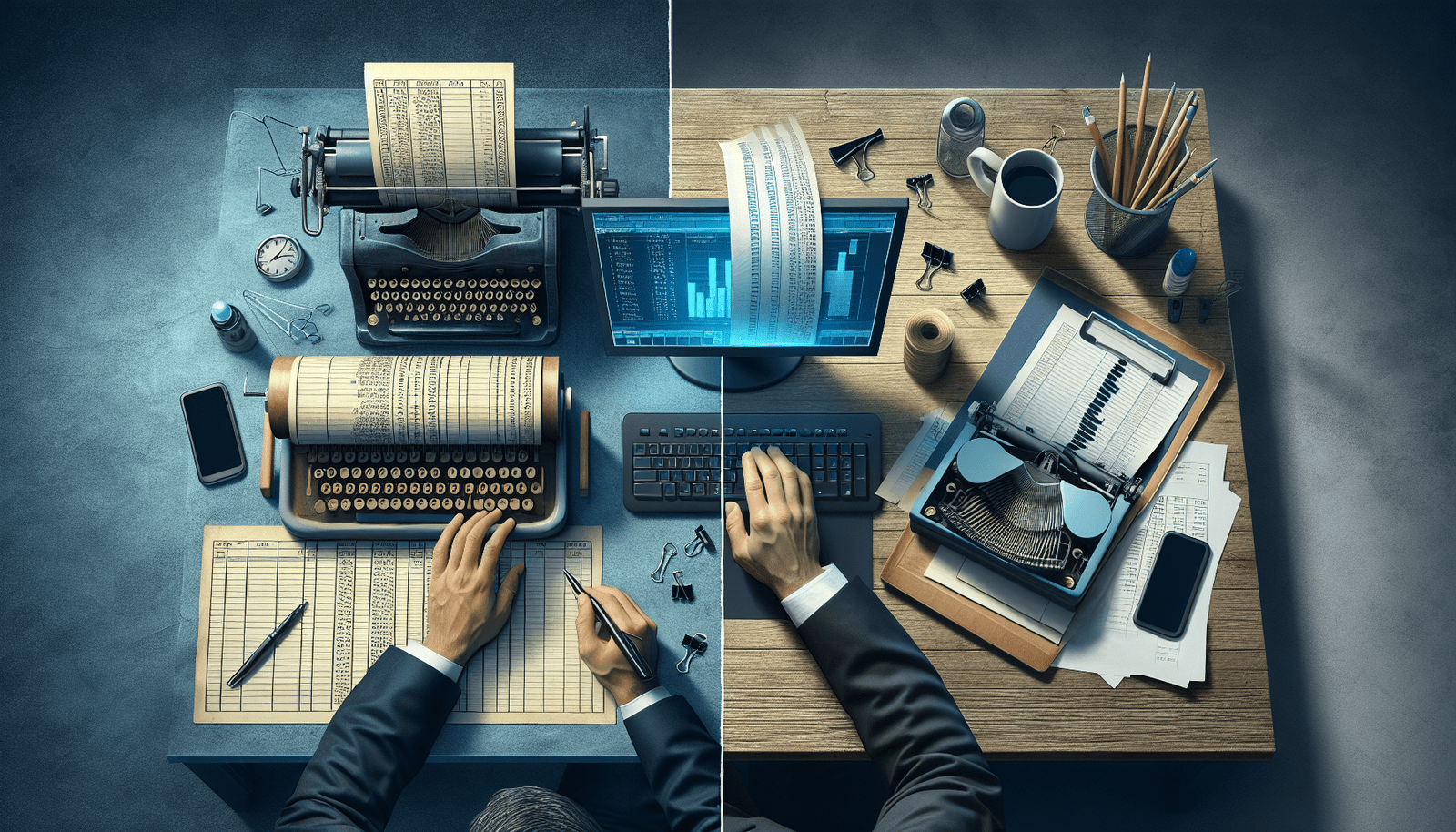
Accounting systems are fundamental tools used for recording, summarizing, and analyzing financial transactions. The evolution from manual to computerized accounting systems marks a significant shift in how businesses manage their financial data. Understanding the core differences between these two methods is crucial for appreciating the advancements in accounting practices.
Manual accounting refers to the traditional method of recording financial transactions by hand. This process involves using physical books or ledgers where entries are made manually, typically through pen and paper or typewriters. Each transaction recorded in various journals and ledgers, requiring meticulous attention to detail to ensure accuracy. Manual accounting relies heavily on the accountant’s skill and precision, making it a time-consuming and labor-intensive process.
In contrast, computerized accounting employs software and digital tools to handle financial transactions. These systems automate many of the tasks that performed manually, such as data entry, calculations, and report generation. Computerized accounting systems store financial data electronically, allowing for quick retrieval and analysis. They also offer features like real-time data processing, advanced reporting capabilities, and integration with other business systems, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
The transition from manual to computerized accounting represents a shift from traditional to modern practices. While manual accounting systems are still in use, especially in smaller enterprises or in regions with limited access to technology, computerized systems have become the standard in most industries. This shift underscores the importance of technology in streamlining business operations and improving financial management.
Overall, the fundamental difference between manual and computerized accounting systems lies in the methods and tools used to record and manage financial transactions. Manual systems rely on physical documentation and human effort. While computerized systems leverage digital technology to automate and enhance accounting processes. This transition has paved the way for more efficient, accurate, and scalable accounting practices.
Definition of Manual and Computerized Accounting Systems
Manual accounting systems have been the cornerstone of financial management for centuries. These systems rely on paper-based methods, where transactions recorded by hand in journals and ledgers. Each entry is meticulously documented, and physical receipts stored as proof of transactions. The accuracy of a manual accounting system hinges on the diligence and expertise of the accountant. Despite its labor-intensive nature, manual accounting offers a tangible and straightforward approach to financial record-keeping.
In contrast, computerized accounting systems utilize digital tools and software applications to manage financial data. Software like QuickBooks, SAP, and Microsoft Excel streamline the accounting process by automating data entry, calculations, and report generation. These systems offer enhanced accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility compared to their manual counterparts. The integration of technology into accounting practices has revolutionized the field. Making it easier for businesses to track and analyze their financial health in real-time.
The evolution from manual to computerized accounting systems marks a significant milestone in the history of accounting. Initially, businesses relied solely on manual methods, which, while effective, were time-consuming and prone to human error. The advent of computerized systems in the late 20th century introduced a paradigm shift, offering unprecedented levels of precision and speed. Today, computerized accounting systems are widely adopted across various industries, reflecting the ongoing digital transformation in the business world.
Understanding the distinctions between manual and computerized accounting systems is crucial for grasping their respective roles in modern accounting practices. While manual accounting provides a fundamental approach rooted in tradition, computerized accounting leverages technology to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Together, they represent the past and present of financial record-keeping, offering valuable insights into the dynamic nature of the accounting profession.
Comparison Table of the Differences Between Manual and Computerized Accounting Systems
Understanding the contrasts between manual and computerized accounting systems is essential for businesses to make informed decisions. Below is a comprehensive comparison table that highlights the key differences between these two systems. Each aspect of comparison is briefly explained to give readers a quick and clear understanding of the practical implications of choosing one system over the other.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Manual Accounting | Computerized Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Prone to human error | High accuracy due to automated calculations |
| Speed | Time-consuming | Fast data processing and report generation |
| Cost | Lower initial cost but higher long-term labor costs | Higher initial setup cost but lower long-term operational costs |
| Data Security | Susceptible to loss, damage, and unauthorized access | Enhanced security with electronic storage and backup solutions |
| Ease of Access | Limited to physical location and office hours | Accessible from anywhere with internet connectivity |
| Scalability | Difficult to scale efficiently | Easily scalable to handle growing business needs |
| Error Checking | Manual reconciliation required | Automated error checking and alerts |
| Storage | Requires physical storage space | Digital storage saves space and is more secure |
| Report Generation | Manual, time-consuming process | Automated, instant generation of detailed reports |
| Compliance | Manual compliance checking | Built-in compliance features |
This table effectively encapsulates the fundamental differences between manual and computerized accounting systems, providing a clear and concise reference for businesses considering which system to adopt. By examining aspects such as accuracy, speed, cost, data security, ease of access, and scalability, stakeholders can better understand the practical benefits and limitations of each accounting method.
Key Differences Between Manual and Computerized Accounting Systems
In the realm of accounting, the choice between manual and computerized systems can significantly impact the efficiency and accuracy of financial operations. Both systems come with their unique set of advantages and limitations, which can influence business operations and financial reporting.
Manual accounting systems, which rely heavily on physical records and handwritten entries, offer a high degree of control over financial data. They are often perceived as straightforward and cost-effective for small businesses with limited transactions. However, the manual nature of these systems makes them susceptible to human error, which can lead to inaccuracies in financial reports. Additionally, the time-consuming process of entering data and reconciling accounts can slow down business operations, particularly as the volume of transactions increases.
On the other hand, computerized accounting systems leverage software solutions to automate and streamline accounting tasks. These systems significantly reduce the potential for human error by automating data entry and calculations. The efficiency gained through automation allows for quicker data processing and more timely financial reporting. Furthermore, computerized systems often come with built-in compliance features that help businesses adhere to regulatory requirements with greater ease.
Data storage and retrieval also present a stark contrast between the two systems. In manual accounting, physical storage of paper records can be cumbersome and prone to risks such as loss, damage, or unauthorized access. Conversely, computerized systems store data electronically, ensuring that information is easily retrievable and secure. Advanced backup solutions further protect data from potential loss or corruption.
While computerized accounting systems offer numerous advantages, they also come with their own set of challenges. Initial setup costs can be high, and businesses may need to invest in training for staff to effectively use the software. Additionally, reliance on technology introduces risks related to system failures or cyber threats, necessitating robust IT support and security measures.
Ultimately, the decision between manual and computerized accounting systems should be based on a comprehensive evaluation of a business’s specific needs, transaction volume, and available resources. By understanding the key differences, businesses can make informed choices that support their operational efficiency and financial accuracy.

Leave a Reply