Importance and Process of Decision-Making; As a leader, you will make decisions involving not only yourself but the morale and welfare of others. Some decisions, such as when to take a break or where to hold a meeting, are simple decisions which have little effect on others. Other decisions are often more complex and may have a significant impact on many people. Therefore, having decision-making, the problem-solving process can be a helpful tool. Such a process can help you to solve these different types of situations.
Here are explain; What is the importance and process of Decision-Making?
Within business and the military today, leaders at all levels use some form of decision-making, problem-solving process. There are several different approaches (or models) for decision-making and problem-solving. We would briefly discuss it in this lesson as well. It is beyond doubt that decision making is an essential part of every function of management.
According to Peter F. Drucker,
“Whatever a manager does, he does through decision making.”
Decision making lies deeply embedded in the process of management, spreads over all the managerial functions and covers all the areas of the organization. Management and decision making are bound up and go side by side in every activity performed by the manager. Whether knowingly or unknowingly, every manager makes decisions constantly. Right from the day when the size of the organization used to be very small to the present day huge or mega-size of the organization, the importance of decision making has been there.
The significant difference is that in today’s complex organization structure, the decision making is getting more and more complex. Whatever a manager does, he does through making decisions.
Importance of Decision-Making:
Some of the decisions are of routine and repetitive in nature and it might be that the manager does not realize that he is taking decisions whereas, other decisions which are of strategic nature may require a lot of systematic and scientific analysis. The fact remains that management is always a decision making the process. The most outstanding quality of a successful manager is his/her ability to make sound and effective decisions.
A manager has to make up his/her mind quickly on certain matters. It is not correct to say that he has to make spur of the moment decisions all the time. For taking many decisions, he gets enough time for careful fact-finding, analysis of alternatives and choice of the best alternative.
Decision making is a human process. When one decides, he chooses a course alternative which he thinks is the best. Decision making is a proper blend of thinking, deciding and acting. An important executive decision is only one event in the process which requires a succession of activities and routine decisions all along the way.
Decisions also have a time dimension and a time lag. A manager takes time to collect facts and to weigh various alternatives. Moreover, after decides, it takes still more time to carry out a decision and, often, it takes longer before he can judge whether the decision was good or bad. It is also very difficult to isolate the effects of any single decision.
What is the process of Decision-Making?
The following procedure should follow in arriving at a correct decision:
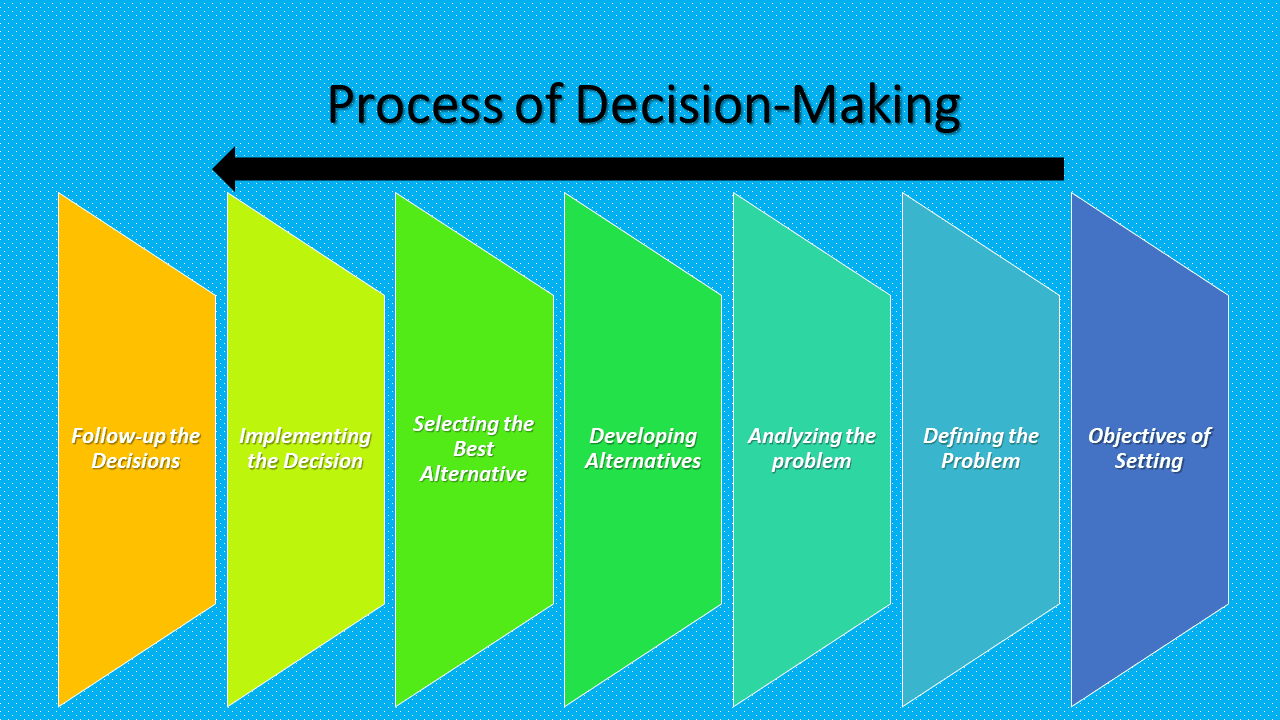
Objectives of Setting:
Rational decision-making involves concrete objectives. So the first step in decision-making is to know one’s objectives. An objective is an expected outcome of future actions. So before deciding upon the future course of efforts, it is necessary to know beforehand what we are trying to achieve. Exact knowledge of goals and objectives bring purpose in planning and harmony in efforts. Moreover, objectives are the criteria by which final outcome is to measure.
Defining the Problem:
It is true to a large extent that a problem well defined is half solving. A lot of bad decisions are made because the person making the decision does not have a good grasp of the problem. It is essential for the decision-maker to find and define the problem before he takes any decision. Sufficient time and energy should be spent on defining the problem as it is not always easy to define the problem and to see the fundamental thing that is causing the trouble and that needs correction.
Practically, no problem ever presents itself in a manner that an immediate decision may take. It is, therefore, essential to define the problem before any action takes, otherwise, the manager will answer the wrong question rather than the core problem. Clear definition of the problem is very important as the right answer can find only to the right question.
Analyzing the problem:
After defining the problem, the next step in decision-making is analyzing it. The problem should thoroughly analyze to find out adequate background information and data relating to the situation. The problem should divide into many sub-problems and each element of the problem must investigate thoroughly and systematically. There can be a number of factors involving any problem, some of which are pertinent and others are remote.
These pertinent factors should discuss in depth. It will save time as well as money and efforts. In order to classify any problem, we require a lot of information. So long as the required information is not available, any classification would be misleading. This will also have an adverse impact on the quality of the decision. Trying to analyze without facts is like guessing directions at a crossing without reading the highway signboards.
Thus, the collection of the right type of information is very important in decision making. It would not be an exaggeration to say that a decision is as good as the information on which it is based. Collection of facts and figures also requires certain decisions on the part of the manager. He must decide what type of information he requires and how he can obtain this.
Developing Alternatives:
After defining and analyzing the problem, the next step in the decision-making process in the development of alternative courses of action. Without resorting to the process of developing alternatives, a manager is likely to guide by his limited imagination. It is rare for alternatives to be lacking for any course of action. But sometimes a manager assumes that there is only one way of doing a thing.
Main Points;
In such a case, what the manager has probably not done is to force himself to consider other alternatives. Unless he does so, he cannot reach the decision which is the best possible.
- From this can derive a key planning principle which may term as the principle of alternatives. Alternatives exist for every decision problem. Effective planning involves a search for the alternatives towards the desired goal.
- Once the manager starts developing alternatives, various assumptions come to his mind, which he can bring to the conscious level. Nevertheless, the development of alternatives cannot provide a person with the imagination, which he lacks. But most of us have definitely more imagination than we generally use.
- It should also note that the development of alternatives is no guarantee of finding the best possible decision, but it certainly helps in weighing one alternative against others and, thus, minimizing uncertainties. While developing alternatives, the principle of limiting factor has to take care of.
- A limiting factor is one which stands in the way of accomplishing the desired goal. It is a key factor in decision making. If such factors are properly identified, the manager can confine his search for an alternative to those which will overcome the limiting factors.
- In choosing from among alternatives, the more an individual can recognize those factors which are limiting or critical to the attainment of the desired goal the more clearly and accurately he or she can select the most favorable alternatives.
Selecting the Best Alternative:
After developing alternatives one will have to evaluate all the possible alternatives in order to select the best alternative. There are various ways to evaluate alternatives. The most common method is through intuition, i.e., choosing a solution that seems to be good at that time.
There is an inherent danger in this process because a manager’s intuition may be wrong on several occasions. The second way to choose the best alternative is to weigh the consequences of one against those of the others. Peter F. Drucker has laid down four criteria in order to weigh the consequences of various alternatives.
They are:
Risk:
A manager should weigh the risks of each course of action against the expected gains. As a matter of fact, risks are involved in all the solutions. What matters is the intensity of different types of risks in various solutions.
The economy of effort:
The best manager is one who can mobilize the resources for the achievement of results with the minimum of efforts. The decision to choose should ensure the maximum possible economy of efforts, money and time.
Situation or Timing:
The choice of a course of action will depend upon the situation prevailing at a particular point of time. If the situation has great urgency, the preferable course of action is one that alarms the organization that something important is happening. If a long and consistent effort is needed, a slow start gathers momentum approach may be preferable.
Limitation of Resources:
In choosing among the alternatives, primary attention must give to those factors that are limiting or strategic to the decision involved. The search for limiting factors in decision-making should be a never-ending process. Discovery of the limiting factor lies at the basis of selection from the alternatives and hence of planning and decision making.
There are three bases which should follow for the selection of alternatives and these are experience, experimentation and research and analysis which are discussed below:
- In making a choice, a manager is influenced to a great extent by his past experience. He can give more reliance on past experience in case of routine decisions; but in the case of strategic decisions, he should not rely fully on his past experience to reach a rational decision.
- Under experimentation, the manager tests the solution under actual or simulated conditions. This approach has proved to be of considerable help in many cases in test marketing of a new product. But it is not always possible to put this technique into practice, because it is very expensive.
- Research and Analysis are considered to be the most effective technique of selecting among alternatives, where a major decision is involved. It involves a search for relationships among the more critical variables, constraints, and premises that bear upon the goal sought.
Implementing the Decision:
The choice of an alternative will not serve any purpose if it is not put into practice. The manager is not only concerned with making a decision, but also with its implementation. He should try to ensure that systematic steps are taken to implement the decision. The main problem which the manager may face at the implementation stage is the resistance by the subordinates who are affected by the decision.
If the manager is unable to overcome this resistance, the energy and efforts consumed in decision making will go waste. In order to make the decision acceptable, it is necessary for the manager to make the people understand what the decision involves, what is expected to them and what they should expect from the management.

Main Points;
In order to make the subordinates committed to the decision, it is essential that they should allow participating in the decision-making process.
- The managers who discuss problems with their subordinates and give them opportunities to ask questions and make suggestions find more support for their decisions than the managers who don’t let the subordinates participate.
- The area where the subordinates should participate in the development of alternatives. They should encourage to suggest alternatives. This may bring to surface certain alternatives which may not be thought of by the manager. Moreover, they will feel attached to the decision.
- At the same time, there is also a danger that a group decision may be poorer than the one-man decision. Group participation does not necessarily improve the quality of the decision, but sometimes impairs it.
- Someone has described group decision like a train in which every passenger has a brake. It has also been pointing out that all employees are unable to participate in decision making. Nevertheless, it is desirable if a manager consults his subordinates while making a decision.
Follow-up the Decisions:
Kennetth H. Killer, has emphatically written in his book that it is always better to check the results after putting the decision into practice.
He has given reasons for following up of decisions and they are as follows:
- If the decision is a good one, one will know what to do if faced with the same problem again.
- If the decision is a bad one, one will know what not to do the next time.
- The decision is bad and one follows-up soon enough, corrective action may still be possible.
In order to achieve proper follow-up, the management should devise an efficient system of feedback information. This information will be very useful in taking the corrective measures and in taking the right decisions in the future.